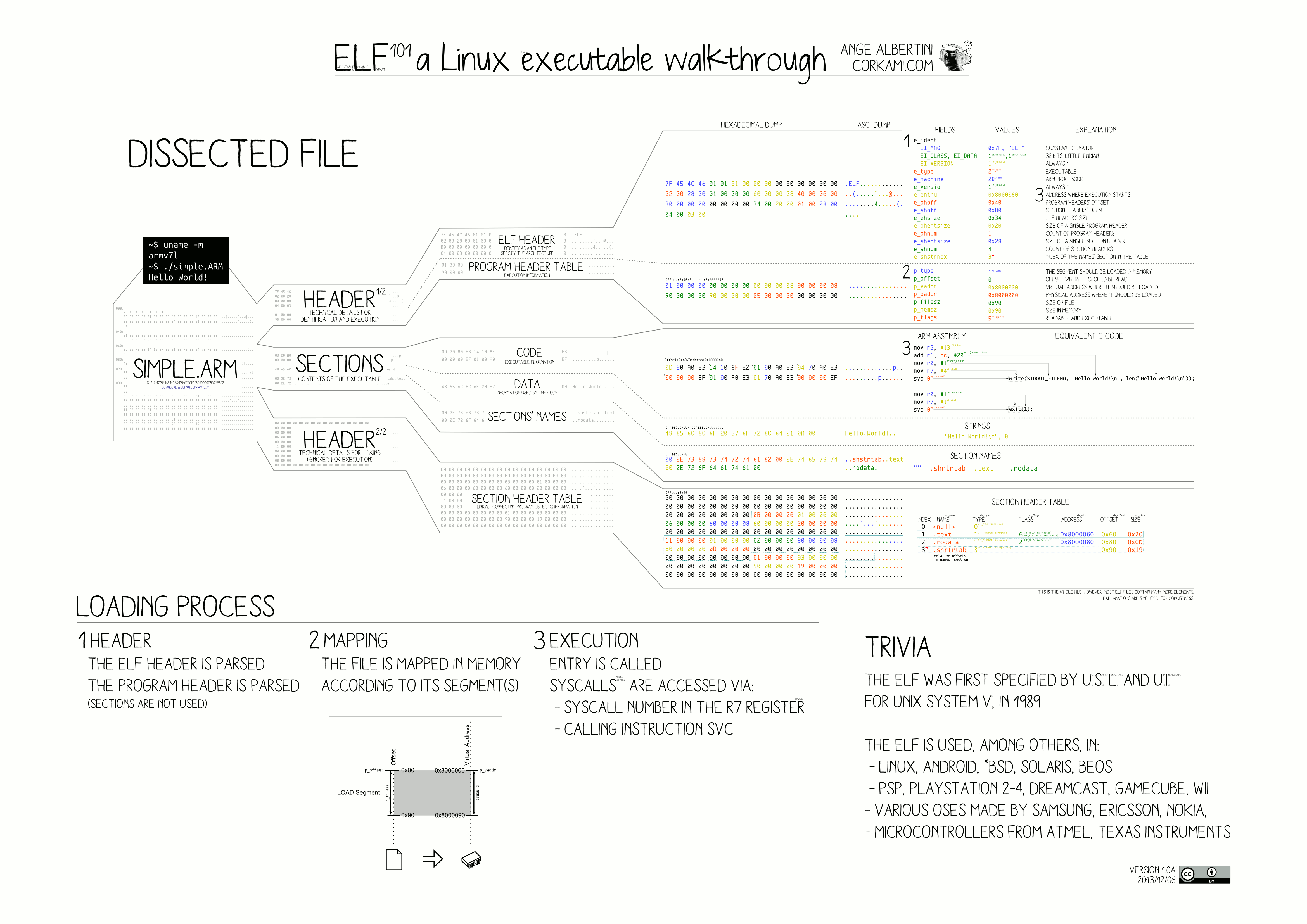
ELF文件解析
关于ELF文件我们可以看下面这张大图(总结地很到位)
Note:
由于目前x86 64位架构为主流,后续分析主要是基于Elf64进行分析、介绍
Demo 源代码地址
结构体介绍
文件包含(usr/include/elf.h)
准备工作
1 2 3 4 5 #include <stdio.h> int main () { printf ("Hello World!" ); }
Elf64_Ehdr
结构体
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #define EI_NIDENT (16) typedef struct { unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; Elf64_Half e_type; Elf64_Half e_machine; Elf64_Word e_version; Elf64_Addr e_entry; Elf64_Off e_phoff; Elf64_Off e_shoff; Elf64_Word e_flags; Elf64_Half e_ehsize; Elf64_Half e_phentsize; Elf64_Half e_phnum; Elf64_Half e_shentsize; Elf64_Half e_shnum; Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; } Elf64_Ehdr;
实际文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ➜ build readelf -h test ELF Header: Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 Class: ELF64 Data: 2's complement, little endian Version: 1 (current) OS/ABI: UNIX - System V ABI Version: 0 Type: DYN (Shared object file) Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64 Version: 0x1 Entry point address: 0x1050 Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file) Start of section headers: 14688 (bytes into file) Flags: 0x0 Size of this header: 64 (bytes) Size of program headers: 56 (bytes) Number of program headers: 11 Size of section headers: 64 (bytes) Number of section headers: 30 Section header string table index: 29
e_ident
e_ident[] Identification Indexes
Name
value
Purpose
EI_MAG0
0
File identification
EI_MAG1
1
File identification
EI_MAG2
2
File identification
EI_MAG3
3
File identification
EI_CLASS
4
File class
EI_DATA
5
Data encoding
EI_VERSION
6
File version
EI_PAD
7
Start of padding bytes
EI_NIDENT
16
Size of e_ident[]
e_type
文件类型
无类型
重定向文件
可执行文件
共享文件
core文件
Processor-specific文件
e_machine
指令集架构
文档中貌似给的不全。
这里我们查表发现是3E,文档中没有记录
e_version
文件版本
e_entry
入口函数地址。
e_phoff Program Header Offeset——其实也就是ELF Header的大小
(引文Elf Header下面就是Program Header )
也就是说0x40开始就是Program Header了
e_shoff
Section Header Offset即0x3960是Section Header的起始地址
但是Section Header貌似是空的。全是0,具体我们后面再分析吧~
e_flags
This member holds processor-specific flags associated with the file. Flag names take the form EF_machine_flag
既然是processor-specs那就是和编译器相关了
e_ehsize
ELF header的大小
e_phentsize
第一个Program Header 的数目
e_phnum
Program Header的数目
e_shentsize
第一个Section Header的大小
e_shnum
Section Header的数目
e_shstrndx
strings table的index下标
Code Practice
读取文件并打印
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 int main () { FILE* fd = fopen("test" , "r" ); struct stat fStatus ; if (fstat(fileno(fd),&fStatus) == -1 ) { printf ("Error fstat!!" ); exit (1 ); }; int len = fStatus.st_size; if (len <= 0 ) { printf ("Error get file len" ); exit (1 ); } char * buf = (char *) malloc (len); int readLen = fread(buf,1 ,len,fd); printfElf(buf,readLen); free (buf); }
打印ELF文件的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void printfElf (void *buf,int len) { Elf64_Ehdr * elf = (Elf64_Ehdr*) buf; printfElfHeader(elf); }
打印Elf Header
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 void printfElfHeader (Elf64_Ehdr* header) { printf ("\n这是Elf Header参数" ); printf ("\ne_ident:\t" ); unsigned char *a = header->e_ident; for (int i = 0 ;i < 16 ; i++) { printf ("%02X " ,a[i]); } printf ("\ne_type: \t%02X" ,header->e_type); printf ("\ne_machine:\t%02X" ,header->e_machine); printf ("\ne_version:\t%04X" ,header->e_version); printf ("\ne_entry:\t%08X" ,header->e_entry); printf ("\ne_phoff:\t%08X" ,header->e_phoff); printf ("\ne_shoff:\t%08X" ,header->e_shoff); printf ("\ne_flags:\t%04X" ,header->e_flags); printf ("\ne_ehsize:\t%02X" ,header->e_ehsize); printf ("\ne_phentsize:\t%02X" ,header->e_phentsize); printf ("\ne_phnum:\t%02X" ,header->e_phnum); printf ("\ne_shentsize:\t%02X" ,header->e_shentsize); printf ("\ne_shnum:\t%02X" ,header->e_shnum); printf ("\ne_shstrndx:\t%02X" ,header->e_shstrndx); }
输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 这是Elf Header参数 e_ident: 7F 45 4 C 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 e_type: 03 e_machine: 3 E e_version: 0001 e_entry: 00001050 e_phoff: 00000040 e_shoff: 00003960 e_flags: 0000 e_ehsize: 40 e_phentsize: 38 e_phnum: 0B e_shentsize: 40 e_shnum: 1 E e_shstrndx: 1 D
Elf64_Shdr
An object file’s section header table lets one locate all the file’s sections. The section header table is an array of Elf32_Shdr structures as described below. A section header table index is a subscript into this array. The ELF header’s e_shoff member gives the byte offset from the beginning of the file to the section header table; e_shnum tells how many entries the section header table contains; e_shentsize gives the size in bytes of each entry. Some section header table indexes are reserved; an object file will not have sections for these special indexes
section header table是一个arr数组。
elf header中 e_shoff字段告诉我们从文件起始位置到section header table的偏移量
elf header中 e_shnum字段告诉我们Section header table这个数组有多少元素。
elf header中e_shentsize 字段告诉我们Section header table中每个元素有多大
其中有部分Sections下标是预留的,也就是没有任何意义的
Sections header结构体
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 typedef struct { Elf64_Word sh_name; Elf64_Word sh_type; Elf64_Xword sh_flags; Elf64_Addr sh_addr; Elf64_Off sh_offset; Elf64_Xword sh_size; Elf64_Word sh_link; Elf64_Word sh_info; Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; } Elf64_Shdr;
sh_name
Section的名称,不过是一个int值,这个值对应string table的index值
String table是一个Section,这个Sections的index在ELF Header的e_shstrndx参数中
String table,紧凑地存放了很多的字符串。
就像这样,’\0’表明一段字符的结束。
那么问题来了,如何使用sh_name index去找指定的字符串。
1.sh_name 的index表明我从string table的指定下标开始,一直往后拼接,直到’\0’所组成的字符串
2.加入sh_name = 7在上图的String Table所代指的String就是从index 为 7 的下标开始,连续拼接。
‘V’,’a’,’r’,’i’,’a’,’b’,’l’,’e’到达’\0’停止,也就是说7代指的”Variable”字符串
同理如下索引都是正确的。
sh_type
Section的类型
sh_flags
sh_addr
如果Section会加载到内存中,sh_addr则是加载后的内存地址,如果不用加载到内存中。则sh_addr的值为0.
sh_offset
Section的第一个字节在ELF文件中的偏移量。
sh_size
Section大小
sh_link
依赖Section类型,参数值为依赖的Section的index值。
sh_info
额外信息
The section header index of the section to which the relocation applies.
sh_addralign
部分Section有对齐的需求。
其中有两个值比较特殊,0,1表示没有对齐的需求(可直接忽略这个字段)。
sh_entsize
有部分的Section可能包含固定长度的Section,sh_entsize用于记录固定Section大小的大小。
如果值为0表示,Section大小不固定。
Code Practice 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 void printfSectionHeaders (Elf64_Ehdr* header) { void * h = (void *) header; printf ("\n\n如下是Elf Sections Header" ); Elf64_Off offset = header->e_shoff; int n = header->e_shnum; Elf64_Shdr* section = (Elf64_Shdr*)(h + offset); printf ("\n%-03s %-018s %-08s %-016s %-016s %-08s %-016s %-016s %-08s %-016s %-016s" ,"idx" ,"name" ,"type" ,"flag" ,"execAddr" ,"offset" ,"size" ,"link" ,"info" ,"align" ,"entrySize" ); Elf64_Shdr* strSectionHeader = section + header->e_shstrndx; char * strSection = h + strSectionHeader->sh_offset; for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i++) { printfSectionHeader(section + i,i,strSection); } } void printfSectionHeader (Elf64_Shdr* header,int index,char * strSection) { Elf64_Word name = header->sh_name; Elf64_Word type = header->sh_type; Elf64_Xword flag = header->sh_flags; Elf64_Addr execAddr = header->sh_addr; Elf64_Off fileOffset = header->sh_offset; Elf64_Xword size = header->sh_size; Elf64_Word link = header->sh_link; Elf64_Word info = header->sh_info; Elf64_Xword align = header->sh_addralign; Elf32_Xword entrySize = header->sh_entsize; printf ("\n%03d %-018s %08x %016x %016x %08x %016x %016x %08x %016x %016x" ,index,strSection + name,type,flag,execAddr,fileOffset,size,link,info,align,entrySize); }
输出结果
Sections String Table
具体的有.strtab\.shstrtab\.dynstr
单纯的字符串数据表
具体实例可见sh_name
Symbol Table
具体的Section有.symtab
数据结构如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef struct { Elf64_Word st_name; unsigned char st_info; unsigned char st_other; Elf64_Section st_shndx; Elf64_Addr st_value; Elf64_Xword st_size; } Elf64_Sym;
同Elf64_Shdr sh_name
定义符号类型 (Symbol Type)& 符号关联(Symbol Binding)
Symbol Binding
STB_LOCAL
局部Symbol
STB_GLOBAL
全局Symbol
STB_WEAK
可认为是全局Symbol,但是定义的优先级更低。
Symbol Type
STT_NOTYPE
类型未声明
STT_OBJECT
类型为数据类型,array,etc…
STT_FUNC
类型为函数类型
STT_SECTION
Symbol关联为一个Section
STT_FILE
Symbol关联为一个File
STT_LOPROC & STT_HIPROC
Symbol Visibility
Symbol和具体Section的归属关系
要依据具体section
对于relocation files
section index如果是SHN_COMMON value值为align限制
section index如果是section下标,value值为Symbol在section offset
对于可执行文件 & shared object
Symbol大小,0表示大小不定。
Code Practice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 void printfSection (Elf64_Ehdr* ehdr, Elf64_Shdr* shdr) { char * sectionName = shstrTab + shdr->sh_name; void * header = ehdr; void * sectionBegin = header + shdr->sh_offset; if (shdr->sh_type == SHT_SYMTAB) { printf ("\n\nSection %s :" ,sectionName); printfSymTabSection(sectionBegin,shdr->sh_size / shdr->sh_entsize); } } void printfSymTabSection (Elf64_Sym* symbol,int n) { printf ("\n%-3s %-38s %-8s %-8s %-8s %-16s %-16s" ,"idx" ,"name" ,"info" ,"other" ,"shndx" ,"value" ,"size" ); for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i++) { Elf64_Sym* cur = symbol + i; Elf64_Word name = cur->st_name; unsigned char info = cur->st_info; unsigned char other = cur->st_other; Elf64_Section shndx = cur->st_shndx; Elf64_Addr value = cur->st_value; Elf64_Xword size = cur->st_size; printf ("\n%-3d %-38s %-8x %-8x %-8x %-16x %-16x" ,i,strTab + name,info,other,shndx,value,size); } }
输出结果
Relocation Table
结构体
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 typedef struct { Elf64_Addr r_offset; Elf64_Xword r_info; } Elf64_Rel; typedef struct { Elf64_Addr r_offset; Elf64_Xword r_info; Elf64_Sxword r_addend; } Elf64_Rela;
针对于relocatable files值是section开始位置到重定位地址的偏移量。
对于可执行文件和so值为重定位地址。
符号表的下标 + 重定向的类型
用于重定位的额外的加数
Code Practice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void printfRelaTabSection (Elf64_Ehdr* ehdr, Elf64_Shdr* shdr) { for (int i = 0 ;i < ehdr->e_shnum; i++) { Elf64_Shdr* sectionHeader = shdr + i; if (sectionHeader->sh_type == SHT_RELA) { char * sectionName = shstrTab + sectionHeader->sh_name; printf ("\n\nSections: %s :" ,sectionName); Elf64_Rela* section = (void *)ehdr + sectionHeader->sh_offset; printf ("\n%-16s %-16s %-16s" ,"offset" ,"info" ,"addend" ); int n = sectionHeader->sh_size / sectionHeader->sh_entsize; for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i++) { Elf64_Rela* rela = section + i; Elf64_Addr offset = rela->r_offset; Elf64_Xword info = rela->r_info; Elf64_Sxword addend = rela->r_addend; printf ("\n%-16lx %-16lx %-16lx" ,offset,info,addend); } } } }
输出结果
Dynamic
如果一个object file参与动态链接过程,那么他就需要有dynamic segment(其中包含.dynamic section)
dynamic section主要用于存放一些动态链接相关的信息。
结构体如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef struct { Elf64_Sxword d_tag; union { Elf64_Xword d_val; Elf64_Addr d_ptr; } d_un; } Elf64_Dyn;
如下是具体的TAG列表。
其中mandatory表示需要含有该类型的列表项。
其中optional表示该类型的列表项是可选的。
DT_NULL
标记Dynamic列表想的结束(没有参数记录列表项的大小)
DT_NEEDED
需要的库的名称,同String Table的引用手段,通过一个index去.dynstr中去寻找。
DT_PLTRELSZ
PLT表的大小(byte)
DT_PLTGOT
Processor-Spec定制的参数,目前发现是用于存放.got.plt section的地址
DT_HASH
存放Symbol hash table的section的地址。
(貌似glibc对这个做了特殊处理,虽然这个东西是mandatory但是在我目前的elf中是不存在的。)
DT_STRTAB、DT_STRSZ
存放.dynstr的起始位置、总大小
DT_SYMTAB、DT_SYMENT
存放.dynsym的起始位置、entry条目大小
DT_RELA、DT_RELASZ、DT_RELAENT
存放.rela.dyn的起始位置、总大小大小(bytes)、rela的entry条目大小(byte)
DT_INIT、DT_FINI
存放init function的位置(.init节)、存放termination funciton的位置(.fini节)
DT_SONAME
存放so的name
DT_RPATH
search path
DT_REL、DT_RELSZ、DT_RELENT
同DT_RELA、DT_RELASZ、DT_RELAENT
DT_PLTREL
保存一个flag,DT_RELA/DT_REL表明当前是在使用.rela还是.rel进行重定位
DT_JMPREL
存放.rela.plt收地址的位置
DT_INIT_ARRAY、DT_INIT_ARRAYSZ、DT_FINI_ARRAY、DT_FINI_ARRAYSZ
存放.init_array的首地址、.init_array大小(bytes)、存放.fini_array的首地址、.fini_array大小(bytes)
DT_DEBUG
用于调试。编译的时候是0,运行的时候会填充为struct r_debug结构体的地址,不做详细介绍,具体可见博客
DT_LOOS through DT_HIOS
保留给操作系统使用。
DT_LOPROC through DT_HIPROC
保留给处理器使用。
Code Practice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void printfDynamic () { int n = ehdr->e_shnum; for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) { Elf64_Shdr* shi = shdr + i; if (strcmp (shstrTab + shi->sh_name,".dynamic" ) == 0 ) { printf ("\n\nSections: %s :" ,shstrTab + shi->sh_name); printf ("\n%-16s %-16s" ,"tag" ,"value" ); Elf64_Dyn* d = (Elf64_Dyn*)((void * )ehdr + shi->sh_offset); while (d->d_tag != DT_NULL) { Elf64_Sxword tag = d->d_tag; Elf64_Xword value = d->d_un.d_val; if (tag == DT_NEEDED) { printf ("\n%-16s %-16s" ,"DT_NEEDED" ,dynStrTab + value); } else if (tag == DT_PLTRELSZ) { printf ("\n%-16s %d bytes" ,"DT_PLTRELSZ" ,value); } ...... d++; } } }
输出结果
Elf64_Phdr
Program Header是用于运行时,操作系统读取创建进程。
数据结构和之前的Section Header有很强的相似性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 typedef struct { Elf64_Word p_type; Elf64_Word p_flags; Elf64_Off p_offset; Elf64_Addr p_vaddr; Elf64_Addr p_paddr; Elf64_Xword p_filesz; Elf64_Xword p_memsz; Elf64_Xword p_align; } Elf64_Phdr;
p_type
描述Segment的类型
PT_NULL
未使用,没有任何意义
PT_LOAD
表示Segment类型为“loadable”,文件内的内容会被加载到Segment开始的位置
PT_DYNAMIC
表示Segment声明了一些动态链接信息。
PT_INTERP
header存储了解释器的大小和路径
PT_NOTE
header存储了note section的大小&位置等辅助信息
PT_SHLIB
保留,展示未分配任何的寓意。
PT_PHDR
声明Program Header的位置和大小
PT_TLS
声明Thread Local Storage的模板
PT_LOOS through PT_HIOS
为操作系统保留的Segment
PT_LOPROC through PT_HIPROC
为处理器预留恶segment
p_flags
权限修饰
p_offset
从文件的第一个字节到指定Segment的offset
p_vaddr
Segment 第一个字节的虚拟地址
p_paddr
声明Segment的物理地址,System V会ignore 这个字段。
这个字段只是给部分操作系统使用的。
p_filesz
Segment在文件中的大小
p_memsz
Segment在“内存”中Segment的大小
p_align
对齐规则,0,1表示没有align限制。
(如果值非0,1必须为2的次方。)
Code Practice 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void printfProgramHeader () { int n = ehdr->e_phnum; printf ("\n\nProgram Headers:" ); printf ("\n%-8s %-8s %-8s %-16s %-16s %-16s %-16s %-16s %-16s" ,"idx" ,"type" ,"flag" ,"offset" ,"vaddr" ,"paddr" ,"filesz" ,"memsz" ,"align" ); for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i++) { Elf64_Phdr* ph = phdr + i; Elf64_Word type = ph->p_type; Elf64_Word flag = ph->p_flags; Elf64_Off offset = ph->p_offset; Elf64_Addr vaddr = ph->p_vaddr; Elf64_Addr paddr = ph->p_paddr; Elf64_Xword filesz = ph->p_filesz; Elf64_Xword memsz = ph->p_memsz; Elf64_Xword align = ph->p_align; printf ("\n%-8d %-8x %-8x %-16lX %-16lX %-16lX %-16lX %-16lX %-16lX" ,i,type,flag,offset,vaddr,paddr,filesz,memsz,align); } }
输出结果
QA .strtab、.dynstr、.shstrtab有什么区别?
共同点:他们都是字符串表、结构相同
差别:
.shstrtab是用来存储section name的
.dynstr是用来存储dynamic 相关的字符串信息
.strtab存储除上述之外的其他信息。
.symtab、.dynsym有什么区别?
都是符号表、 结构一致
.symtab是普通的符号表,用于除开动态链接的其他场景。
.dynsym是动态符号表,主要用于动态链接过程中的重定位操作
.rela.dyn和.rela.plt有什么区别?
都是用于重定向的entry
差别就是.rela.dyn主要用于动态重定位。
.rela.plt主要用于plt表内的重定位
.plt、.plt.got、.got、.got.plt是什么?有什么区别?
.plt用于存放lazy binding 的链接函数
.got.plt用于记录lazy binding 函数的跳转值
.plt.got用于存放不需要lazy binding 的plt 记录。
.got 用于存放全局变量 & 不需要 延迟绑定的函数的地址
参考 维基百科
TIS Portable Formats Specifications
System V ABI
System V,AMD64 Supplement
Github gist
rk700博客