Android ClassLoader加载流程解析
Android ClassLoader加载流程
Note:
本文主要是针对于ClassLoader加载逻辑进行分析,并未对Class define逻辑进行分析。

起点
ClassLoader.load
Class.forName
过程
Java执行过程
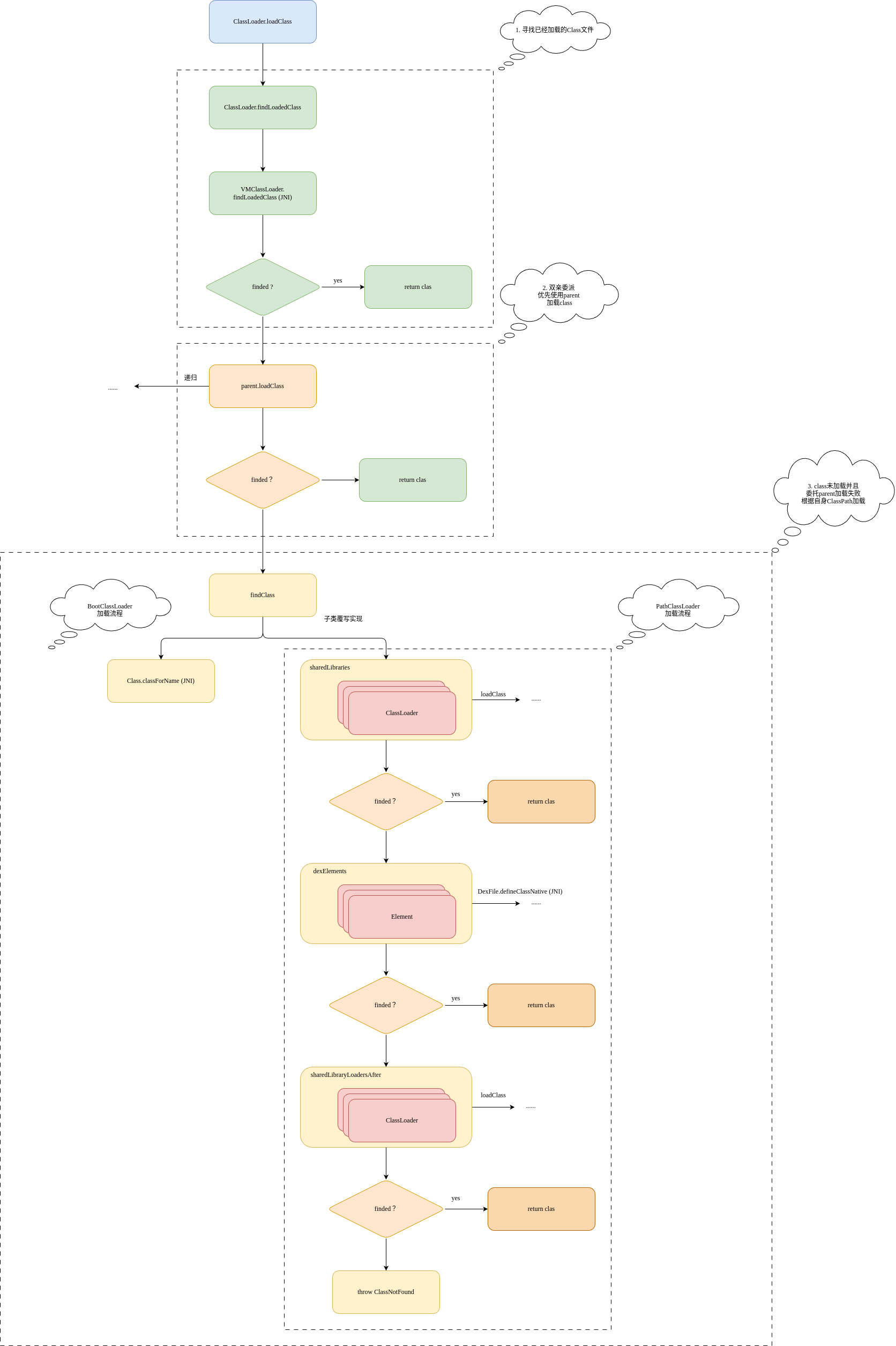
1. ClassLoader.loadClass(String name)
1 | public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { |
2. ClassLoader.loadClass(name, false)
加载流程其实比较固定
- 通过findLoadedClass查看该class是否已经加载过
- 调用parent.loadClass加载class
- 如果#2加载失败通过findClass通过自生加载Class
1 | /** |
2.1 findLoadedClass(name)
这一步对应上述加载流程的的第一步
通过findLoadedClass查看该class是否已经加载过
1 | protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) { |
2.2 parent.loadClass
对应第二步骤。很明显这是一个递归调用。会让loadClass操作流转到parent
然后递归执行loadClass操作
Note: 需要有一点需要注意,如果parent为null会直接return null
1 | if (parent != null) { // parent不为null 调用loadClass |
2.3 findClass
对应上述的第三步。
这方法的原型在ClassLoader.java里面,默认实现是直接跑一场
1 | protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { |
他有两个比较常见的实现类
BootClassLoader.java
约等于Class.forName
1 | protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { |
BaseDexClassLoader.java
从下方代码可以明显看出#1,#2的执行是递归操作
1 |
|
DexPathList.findClass
1 | public Class<?> findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) { |
小结
到此java层的加载流程就结束了。
简单总结下流程
ClassLoader.loadClass(String name) (这个方法没做什么实际操作)
ClassLoader.loadClass(name, false)
a. findLoadedClass => VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass (JNI)
b. parent.loadClass(name, false) (递归)
c. findClass (不同的ClassLoader有不同的是实现,以BaseDexClassLoader为例)
i. sharedLibraryLoaders.loadClass(name) (递归)
ii. pathList.findClass => dexElements.findClass => .. => DexFile.defineClassNative (JNI)
iii. sharedLibraryLoadersAfter.loadClass(name) (递归)
如下是一个简单的流程图(中间省略了一些native实现逻辑,留到后续讲解说明。)
Native执行流程
首先需要明确我们需要分析那些逻辑
- VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass (JNI)
- Class.classForName
- DexFile.defileClassNative
VMClassLoadr.findLoadedClass
方法整体的执行逻辑如下
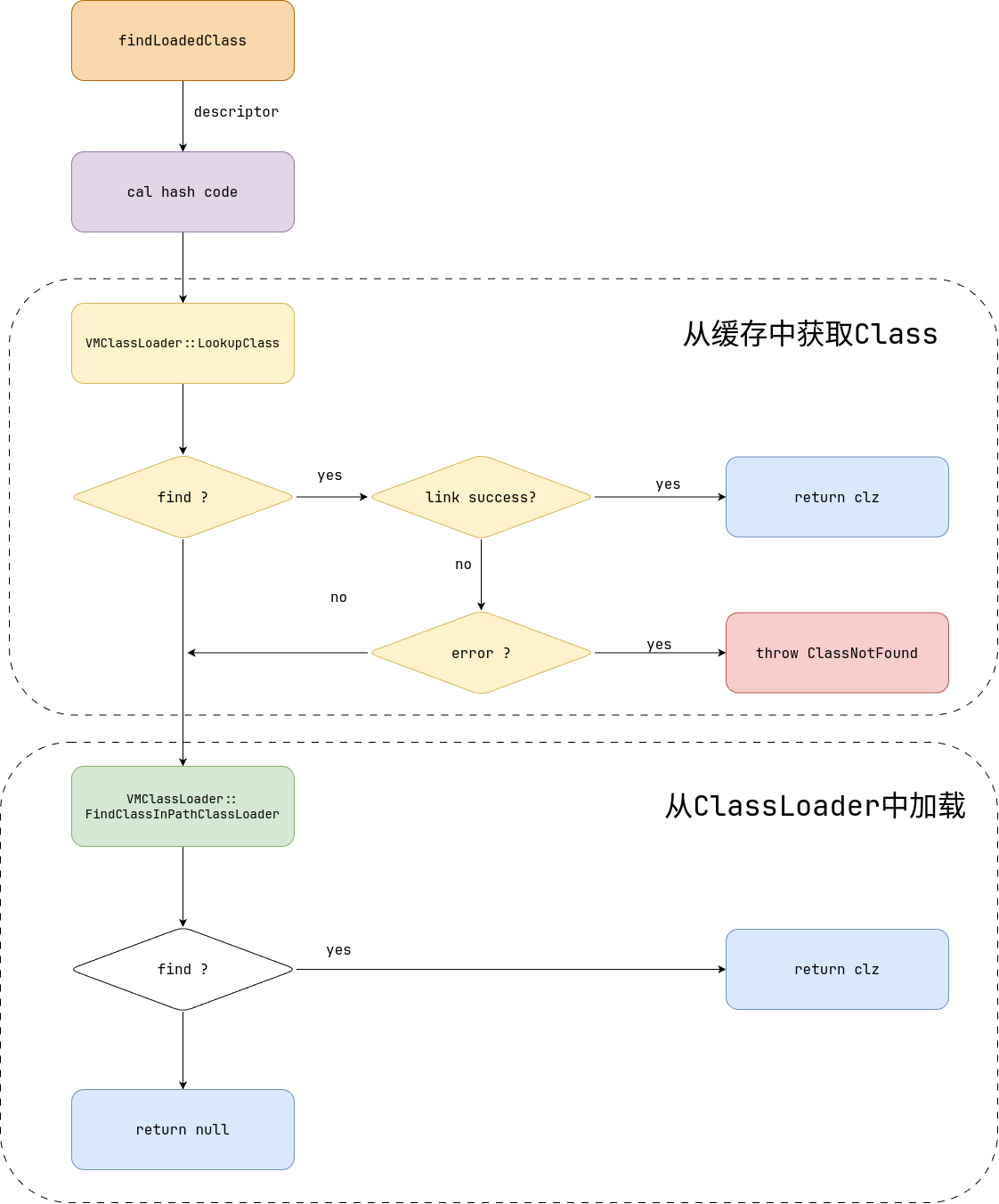
- 计算java name对应的 hash值
- 通过hash值从classloader table中寻找class是否加载过(加载过直接返回)
- 如果class没有加载过,尝试自行加载class
1 | static jclass VMClassLoader_findLoadedClass(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject javaLoader, |
FindClassInPathClassLoader(没有做实际的加载动作)
1 | static ObjPtr<mirror::Class> FindClassInPathClassLoader(ClassLinker* cl, |
FindClassInBaseDexClassLoader
FindClassInBaseDexClassLoader方法本质上是通过ClassLoader进行类加载,但是不是所有的classloader都会在native层直接执行。
(如果是自定义的ClassLoader, 系统也不知道应该怎么加载。因为你可能会破坏原本既定好的加载机制。)
只针对于3种不同类型的ClassLoader做了兼容和处理
ClassLoader 为null or BootClassLoader
a. 直接通过BootClassLoader加载Class
ClassLoader为PathClassLoader, DexClassLoader, InMemoryDexClassLoader
a. 先通过parent classloader进行递归加载
b. 逐一使用shared libraries进行递归加载
c. 使用当前的classloader加载class
d. 使用shared libraries after加载class
ClassLoader为DelegateLastClassLoader
a. 首先使用boot class path加载class
b. 加载使用则使用shared libraries加载
c. 再通过classloader loader本身的path进行加载
d. 最终使用parent进行递归加载。
其他 (对应于自定义的ClassLoader)
a. 直接返回

1 | bool ClassLinker::FindClassInBaseDexClassLoader(ScopedObjectAccessAlreadyRunnable& soa, |
Class.classForName
JNI调用后的方法入口。
只是做了参数的解析,没做实际的操作。
核心逻辑在class_linker->FindClass中
1 | static jclass Class_classForName(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jstring javaName, jboolean initialize, |
ClassLinker::FindClass
代码链路其实比较长
我们可以把整个执行流程分为这么几大类
- 加载基本数据类型
- 计算描述符hash值,从缓存中获取class
- 加载类型不是数组类型 & classloader == null
- 数组类型类加载
- 非数组类型类加载
- 加载完成将class insert到缓存
从如下流程图我们可以很明显知道class for name针对于3种不同的类型进行了单独的处理操作。
基本类型、数组类型、非数组类型。
除此之外就是classl table缓存的获取 & 更新(加载前查缓存,加载后更新缓存)
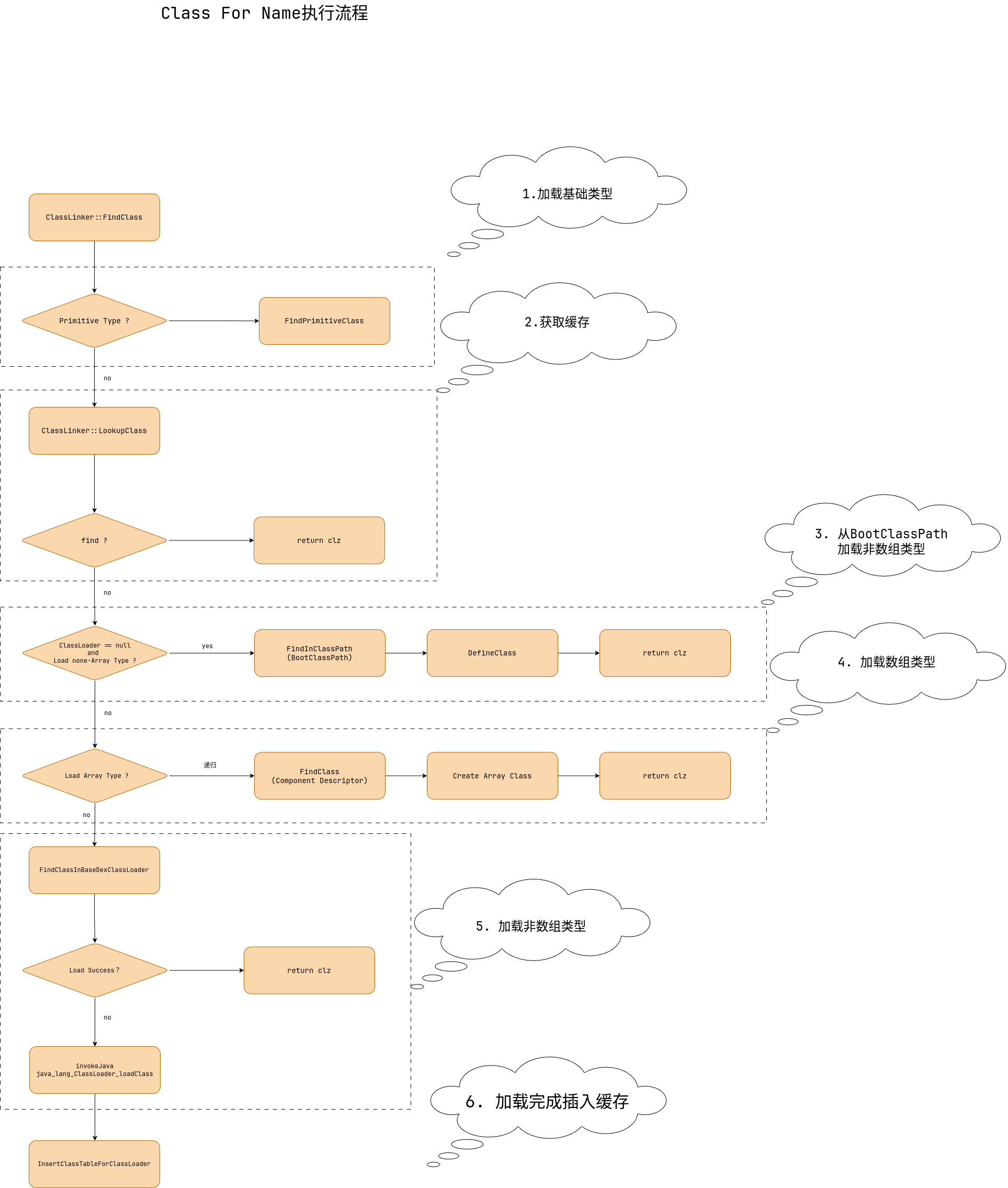
1 | ObjPtr<mirror::Class> ClassLinker::FindClass(Thread* self, |
DexFile.defineClassNative
JNI入口位置
可以简单总结为以下几个过程
将DexFile.mCookie转化为Native DexFile数组
遍历所有的DexFile
a. 调用OatDexFile::FindClassDef加载Class
b. 调用ClassLinker::DefineClass定义Class
c. 调用InsertDexFileInToClassLoader将DexFile插入到ClassLoader中
上述过程中的一些方法其实在之前FindClassInBaseDexClassLoader中也有用到。
所以defineClassNative其实不算是新逻辑。
1 | static jclass DexFile_defineClassNative(JNIEnv* env, |
QA
为什么需要两套类加载机制(Java & Native)
眼尖的小伙伴或许能发现我们流程图中有两个类加载的逻辑。

问题来了,为什么需要设计两套呢?
我自己结合对代码的理解给出一种解释(不一定对):
首先先说结论,出现两套的原因是历史原因,最开始类加载是Java代码 ,后续工程师发现Java代码加载速度比较慢,接着就将一些常用的ClassLoader直接在Native实现了一份以提升性能。因此只有部分我们比较熟知的系统ClassLoader的加载逻辑是走的Native实现,其他的都是走的Java实现。
类加载代码最早是Java代码这点其实不太准确,准确的来说应该是最早是在java层控制类加载的顺序(先从哪里找然后再从哪里找,最后再……)
第二点java代码的执行速度慢这个问题,其实能从代码的注释中发现, FindClassInPathClassLoader是作为一个fast-path, 只有当classloader是系统熟知的一些ClassLoader(PathClassLoader, InMemoryDexClassLoader, BootClassLoader……)才会走对应的逻辑。如果是自定义的ClassLoader将会走Java逻辑代码。
1 | static jclass VMClassLoader_findLoadedClass(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject javaLoader, |
DexElement, DexFile, DexCahe, ClassTable 是什么
refs: https://juejin.cn/post/7047680282463305735?searchId=202503301638213703DE9FA4841F24C422
- DexElement是DexFile的Java表示形式(通过JNI持有native引用。)
1 | // TODO(calin): clean up the unused parameters (here and in libcore). |
- DexFile是”dex文件“的对象形式

DexCache保存dex解析过程中的成员变量,方法,类型,字符串信息。(本文未作讲解)
ClassTable是ClassLoader的类缓存表,用于缓存已经加载类,在类加载过程中用于快速返回结果
ClassLoader.loadClass会通过调用VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass寻找已经加载的所有类的信息。
而findLoadedClass会调用LookupClass从classTable中寻找当前已经加载的类信息。从而快速返回已加载的类。

未完待续……
Class加载原理分析